According to PwC’s Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey 2020, 47% of companies experienced fraud in the past 24 months. The survey found that the most common types of fraud were cybercrime, customer fraud, and asset misappropriation. The total cost of these crimes reached a staggering $42 Billion. Considering that most large enterprises deploy ERP applications to run their financial and purchasing operations, greater visibility and control of transactions that are executed within ERP applications is crucial. Adaptive authentication at the transaction level can provide a simple yet effective control mechanism to detect and prevent financial fraud.
What is Adaptive Authentication?
Also known as dynamic multi-factor authentication (MFA), adaptive authentication allows you to implement MFA challenges based on the user’s risk profile. It allows you to orchestrate security policies that can trigger an MFA challenge based on attributes like location, IP address, time, device type, etc. While most MFA solutions do this when a user logs into the application, implementing MFA at the transaction level for sensitive transactions creates an additional security layer based on the perceived risk of access.
How Transaction Level Adaptive MFA Detects and Prevents Fraud
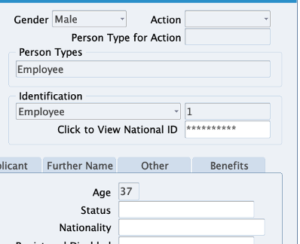
Layered Security: Implementing multi-factor authentication at the transaction level creates a preventive control layer within your ERP applications. For example, sensitive transactions like approval of purchase orders, vendors, or payments can be secured in the event of a breach or stolen user credentials.
Monitoring and Detection: One of the major challenges in ERP applications is gaining visibility into the thousands of transactions that take place every day. With transaction-level MFA, security and audit teams can monitor sensitive, high-value transactions with detailed logs of who is approving what and when. This leads to faster detection of suspicious user activity that could lead to fraud.
Risk Mitigation: With users logging in remotely and through personal devices, adaptive MFA at the application access and transaction-level can be triggered based on contextual risk. This allows organizations to implement multiple control layers to mitigate their overall security and financial risk.
Adaptive Authentication with Appsian Security
The Appsian Security Platform enables organizations to take a risk-based adaptive approach to ERP security. The platform allows you to implement Dynamic Multi-Factor Authentication at the transaction level, creating a logged record of sensitive transactions. Using an attribute-based access control (ABAC) security model, every authentication request is first analyzed for level of risk, and MFA challenges are deployed accordingly. Security teams can also centrally enforce strict identity and device zero-trust policies across multiple ERP applications.
Schedule a demo to find out how Appsian’s enterprise MFA solutions can enhance your fraud prevention and detection capabilities.